Powder Coating Resins and their Properties
Powder coatings are known to be composed of a binding agent, pigments, fillers and additives. Synthetic resins, which act as the binding agent, form the main component (up to 60% of the mixture) and are largely responsible for the properties of the final coating. The hardness and stability as well as the general surface quality are a direct result of the resin that is used. Film formation can occur according to two different mechanisms. These are:
- physical drying
- chemical crosslinking (curing)
Based on their physical and chemical behavior, binding agents are categorized into thermoplastics and thermosets.

Thermosets
Let's start with thermoset powder coatings, also often referred to as thermo-setting coatings. Their chemistry is a blend of resin and hardener that reacts and cures the coating. Once they're set, there's no going back; they won't melt even if things heat up. The magic happens in a special oven during the curing process, where a chemical cross-linking reaction kicks in at just the right temperature. This crosslinking reaction is the secret behind the impressive properties of thermoset powder coatings.
Binding agents:
- Epoxy resin
- Polyester
- Polyurethane
- Acrylate
Thermoplastics
Think of thermoplastic powder coatings as the chameleons of the coating world. Why? They're often used in a process called 'hot dipping,' and here's the cool thing: they can re-melt when exposed to high temperatures and then they can be re-applied. They have a soft and flexible surface, but truth be told, they're not the best at standing up to scratches. Plus, they're not exactly weather-resistant either, which is a big reason why TIGER doesn't produce thermoplastic powder coatings.
Binding agents:
- Polyamide
- PVC
- Polyethylene
- Thermoplastic polyester
Requirements for thermoset powder coating materials
- solid at normal temperatures (melting point > approx. 65 °C)
- melting temperature must not be too high
- low melt viscosity in the standard temperature range for curing
- physically and chemically stable during storage up to at least 40 °C
- good adhesion to various materials without adhesion promoters
- good dyeability

TIGER specializes in the processing of thermosetting resins and even manufactures some of its polyester resins itself in its in-house synthetic resin production facility. This enables us to integrate high quality and specially tailored properties into powder coatings through the resin.
The most important binders at a glance
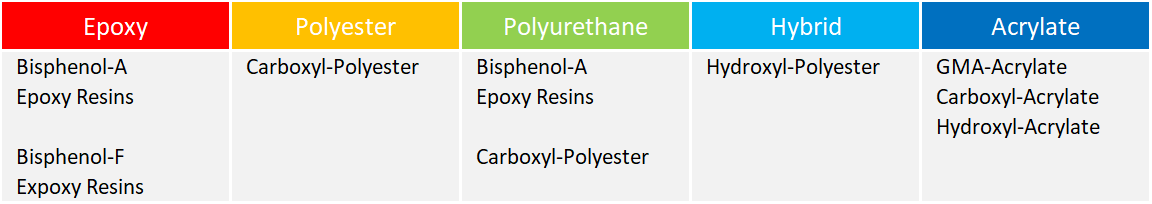
Epoxy Resin
Composition
There are different types of epoxy resins, each offering different functionalities. A large proportion of the epoxy resins used worldwide are based on Bisphenol A.
Crosslinking possibilities of epoxy resins
- Amine (Aliphatic, Cycloaliphatic, Aromatic)
- Anhydrides
- imidazoles
- isocyanates
- silanols
- Aminoplasts (amino or amide resins)
- Phenolic resins (linear phenolic resins, cresol novolaks)
Properties
Epoxy resin has good adhesion to the substrate, excellent mechanical properties (elasticity) and very good chemical resistance. The disadvantage is yellowing and chalking of the surface due to exposure to higher temperatures or UV light.
Although new developments have reduced these disadvantageous properties, epoxy resin is not suitable for high-quality, weather-resistant coatings.
Epoxy resin-based powder coatings provide a very smooth flow for high-gloss and matte surfaces. Due to their crosslinking properties, they are perfectly suited as primers:
- very good penetration into angles and edges
- good chemical resistance
- high reactivity/good low-temperature behavior
Applications
Epoxy powder coatings are therefore used today almost exclusively in the functional sector, e.g. for automotive parts, in the electrical and electronics industry, corrosion protection primers and for fittings and reinforcing iron.
Polyester Resin
Composition
Polyesters are formed as reaction products from the esterification of polyhydric alcohols with polycarboxylic acids.
Crosslinking possibilities of polyester resins
Reactions with carboxylic acid functional polyester resins
- Triglycidyl isocyanurate (TGIC)
- Hydroxyalkylamides (HAA)
- Glycidyl esters
- Epoxy resins (hybrids)
Reactions with hydroxyl-functional polyester resins
- Isocyanates (IPDI adduct)
- Polyuretdiones (polyisocyanates)
Properties
Polyester resins are characterized by particularly high resistance to yellowing and chalking. Due to their temperature stability, they are also being used more and more in interior applications. In addition, they show high gloss and color stability and are suitable for many effects and surfaces.
However, solvent resistance is lower compared to epoxies and hybrids.
Applications
Due to their weather resistance, polyesters are suitable for all outdoor applications such as facade elements, window frames, agricultural equipment, garden and camping furniture, lighting fixtures and two-wheeled vehicles, etc.
Polyurethane Resin
Composition
PUR powder coatings are based on free polyester resins containing hydroxyl groups, which are crosslinked with polyisocyanates by an addition reaction.
Based on derivatives of IPDI (isophorone diisocyanate) there exist mainly two common crosslinking options:
- Isocyanate adducts
- polyisocyanates (polyuretdiones)
Properties
Powder coatings based on polyurethane also show outstanding weathering and chalking resistance. In addition, they have excellent flow and anti graffity properties.
Applications
The field of application of PUR powder coatings is therefore overlapping with that of polyesters. Often when chemical resistance is required, PUR powders are the preferred option. They are especially popular in the rail sector.
Hybrid Systems
Composition
In the production of epoxy resin/polyester mixed powder coatings, so-called hybrids, suitable polyester resins are used, which contain terminal, free carboxyl groups in the molecule, which cause spatial crosslinking via addition to epoxy groups.
The mixing ratio varies from 60:40 to 10:90 of epoxy resin to polyester. (most common mixing ratios 70/30, 60/40 and 50/50) The exact mixing ratio is determined by specific customer requirements and application areas.
Properties
Hybrids have similar properties to epoxy powder coatings but offer better yellowing stability during curing and lower chalking tendency under UV exposure.
Applications
The application areas are mainly found in the decorative sector, store and shelf construction, metal office furniture, household appliances, garden and camping furniture, ceiling elements and radiators.
Acrylic Resin
Composition
The product group of weather-resistant acrylic powder coatings is based on acrylic resins that can be crosslinked with different hardeners.
Crosslinking possibilities of GMA acrylate resins
- aliphatic dicarboxylic acids
- polycarboxylic acids and their anhydrides
- polyanhydrides
- aliphatic diamines
Properties
Acrylic powder coatings have outstanding properties:
- Low-emission and low-waste coating
- Flow comparable to liquid coatings in the automotive industry
- Above-average weather stability (5-year Florida test)
- Crack-free clear coats à No craze cracking
- Curing temperatures of 130 °C possible
Nevertheless, their share of the powder coatings market is lower than for the other binder systems, which can be explained by the following limitations:
- high price
- Not storage stable at room temperature à cooling necessary
- air-conditioned and cleaned air supply necessary
- compatibility à compartmentalization of systems with conventional powder coatings necessary
Back to overview